
When the K-shell electron is ejected from its orbit, an outer-shell electron drops into the open position and creates an energy difference. For a projectile electron to remove this orbital electron, it must possess energy equal to or greater than 69.5 keV. K-shell electrons in tungsten have the strongest binding energy at 69.5 keV. The electron must have enough energy to eject the K-shell electron from its orbit. Electrical current is supplied to the x-ray tube by means of two high-voltage cables that enter the top of the tube assembly.Ĭharacteristic interactions are produced when a projectile electron interacts with an electron from the inner shell (K-shell) of the tungsten atom.

The tube housing is required to allow no more than 100 mR/hr of leakage radiation to escape when measured at 1 m from the source while the tube operates at maximum output. Leakage radiation refers to any x-rays, other than the primary beam, that escape the tube housing. The tube housing is lined with lead to provide additional shielding from leakage radiation. It is the metal tube housing that the radiographer sees and handles when moving the x-ray tube. All of these components are surrounded by metal tube housing except for a port, or window, which allows the primary beam to exit the tube. The purpose of insulating oil is to provide more insulation from electrical shock and to help dissipate heat away from the tube. The envelope serves two additional functions: It provides some insulation from electrical shock that may occur because the cathode and anode contain electrical charges, and it dissipates heat in the tube by conducting it to the insulating oil that surrounds the envelope. The envelope allows air to be evacuated completely from the x-ray tube, which allows the efficient flow of electrons from cathode to anode. The metal tube envelope can collect these electrons and conduct them away from the anode. Off-focus radiation occurs when projectile electrons are reflected and x-rays are produced from outside the focal spot. An additional advantage of a metal envelope is the reduction of off-focus radiation. Replacing all of this section of glass with metal prevents these problems and extends the tube life. This evaporation could affect the flow of electrons and cause the tube to fail. Rotating anode x-ray tubes are used in all applications in radiography, whereas stationary anode tubes are limited to studies of small anatomic structures such as the teeth.įIGURE 2-6 A glass envelope x-ray tube as it appears before installation in a tube housing.Ī disadvantage of a glass envelope x-ray tube is that tungsten evaporated from the filament during exposure can deposit on the inside of the glass, especially in the middle portion of the envelope.
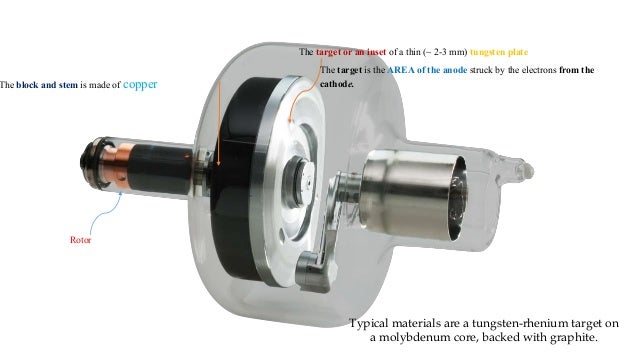
Because of the larger area of the target being bombarded during an exposure, the rotating anode is able to withstand higher heat loads produced by greater exposure factors. The size of the focal spot is not altered with a rotating anode, but the actual physical area of the target bombarded by electrons is constantly changing, causing a greater area-a focal track-to be exposed to electrons. Figure 2-5 shows the stationary anode’s focal spot and the rotating anode with its focal track. With rotating targets, this area is represented by a focal track. With stationary targets, the focal spot is a fixed area on the surface of the target. The ability to withstand high heat loads relates to the actual focal spot, which is the physical area of the target that is bombarded by electrons during x-ray production. Rotating anodes can withstand high heat loads. The radiographer also needs to be aware of the amount of heat that is produced during x-ray production because excessive heat can damage the tube.Īs heat is produced when the x-ray exposure is made, it is transferred to the insulating oil that surrounds the x-ray tube. Kilovoltage peak (kVp), milliamperage (mA), and exposure time all are factors that the radiographer selects on the control panel to produce a quality image. The radiographer controls many of the actions that occur within the tube.

Tungsten disk xray how to#
Radiographers must understand how the x-ray tube is constructed and how to operate it. The x-ray tube is the most important part of the x-ray machine because the tube is where the x-rays are produced.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
